|
Projects |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
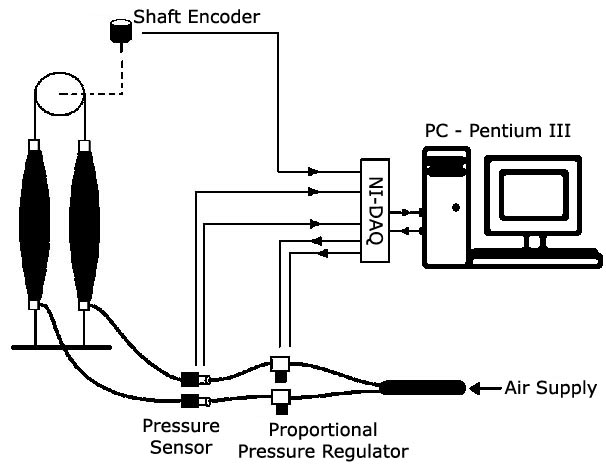
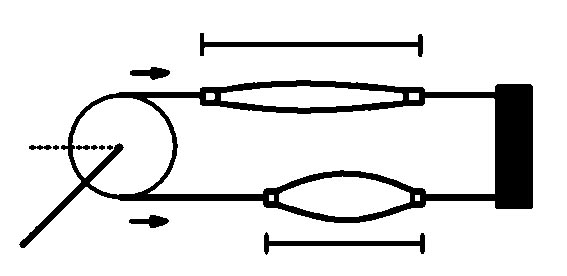
The McKibben Artificial Muscle Actuator is a pneumatic actuator whose properties include a very high force to weight ratio. It was originally developed in artificial limb research. It consists of an internal bladder surrounded by a braided mesh shell (with flexible yet non-extensible threads) that is attached at either ends. When the internal bladder is pressurized, the high pressure pushes against the inner surface and the external shell. However, due to the non-extensibility of the threads in the braided mesh, the actuator shortens to its volume increase and produces a tension when coupled to a mechanical load. The physical configuration of the muscle gives the muscle its variable-stiffness spring like characteristics, non-linear passive elasticity, physical flexibility, and very light weight compared to other kinds of artificial actuators.
Experimental Setup
Videos [New Videos Added!!] Artificial Muscle - Video1 [Video1] Artificial Muscle - Video2 [Video2] Artificial Muscle - Video3 [Video3] Artificial Muscle - Video4 [Video4]
|