|
|
RO-PE III
Specifications
|
Degree Of Freedoms:
Height:
Width:
Weight:
Armor materials:
Sensors:
|
18
580mm
150mm
3.8kg
0.5mm Aluminium (Al) plate
Infra-red x 6
Vision x 1
Magnetic Compass x 1
Gyro x 1 |
Description
RO-PE III is modeled after the systems and design of RO-PE II. It retains the basic operating systems and software but has improved mechanical design and sensors integration.
As such, the control system for RO-PE III is similar to that used in RO-PE II and consists of computer system, sensors and actuators. Followings is a diagram illustrating connection among various elements of the control system.
|
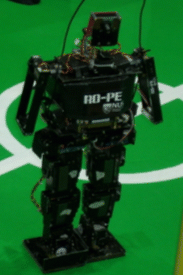
(Top) RO-PE III at RoboCup'05 Osaka, Japan |
Computer Systems
PC-104: RO-PE III runs on a PC-104 processor that is similar to the conventional desktop PC, albeit with slower speed and a hard disk in the form of a compact flash (CF) card.
Data Acquisition (DAQ) card: The PC-104 is connected to the DMM-32-AT DAQ card from Diamond Systems. This DAQ card has 32 analog input ports, 4 analog output ports and 3 digital input/output ports and is used to read analog signals from the sensors.
Operating system: RO-PE III operates on the Real-Time Linux (RT Linux) system, which constantly refreshes the program loop. This allows us to program time-based motion and visual algorithms for the robot. The programming language used in this robot is C.
Sensors
Camera: The primary sensor of the robot is the vision system. We are using the CMU 2 camera developed by Seattle Robotics.
Infra-red (IR): RO-PE III makes use of the Sharp GP2Y0A02YK IR sensor which is an excellent IR sensor that is able to detect obstacle distances accurately. It has a detecting distance of 20cm to 150cm.
Gyro and Compass: The integration of the rate gyroscope (by Silicon Sensing Systems) and Devantech magnetic compass provides an accurate heading for the direction of the robot.
Actuators
All motors used in RO-PE III are the servo motors commonly found in radio-controlled toys like the model helicopter. They are light, durable and provide the high torque needed to lift the limbs of the robot. Most of the servo motors use titanium gears, and are from Hitec.
Control Algorithms
Walking is something that a healthy human being takes for granted but it is essentially a complex sequence of actions.
There are generally two kinds of bipedal walking: static and dynamic walking. The former involves keeping the center of mass within the support area of the feet at all times of motion.
In dynamic walking, we shift of the center of mass out of the support area and use the swing leg to break the fall. This will allow us to make use of the momentum garnered from the motion to move the robot.
Static walking is implemented for RO-PE III. The inverse kinematics model is used to calculate the turning angle of every servo motor to achieve certain joint positions. |