|
Projects |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
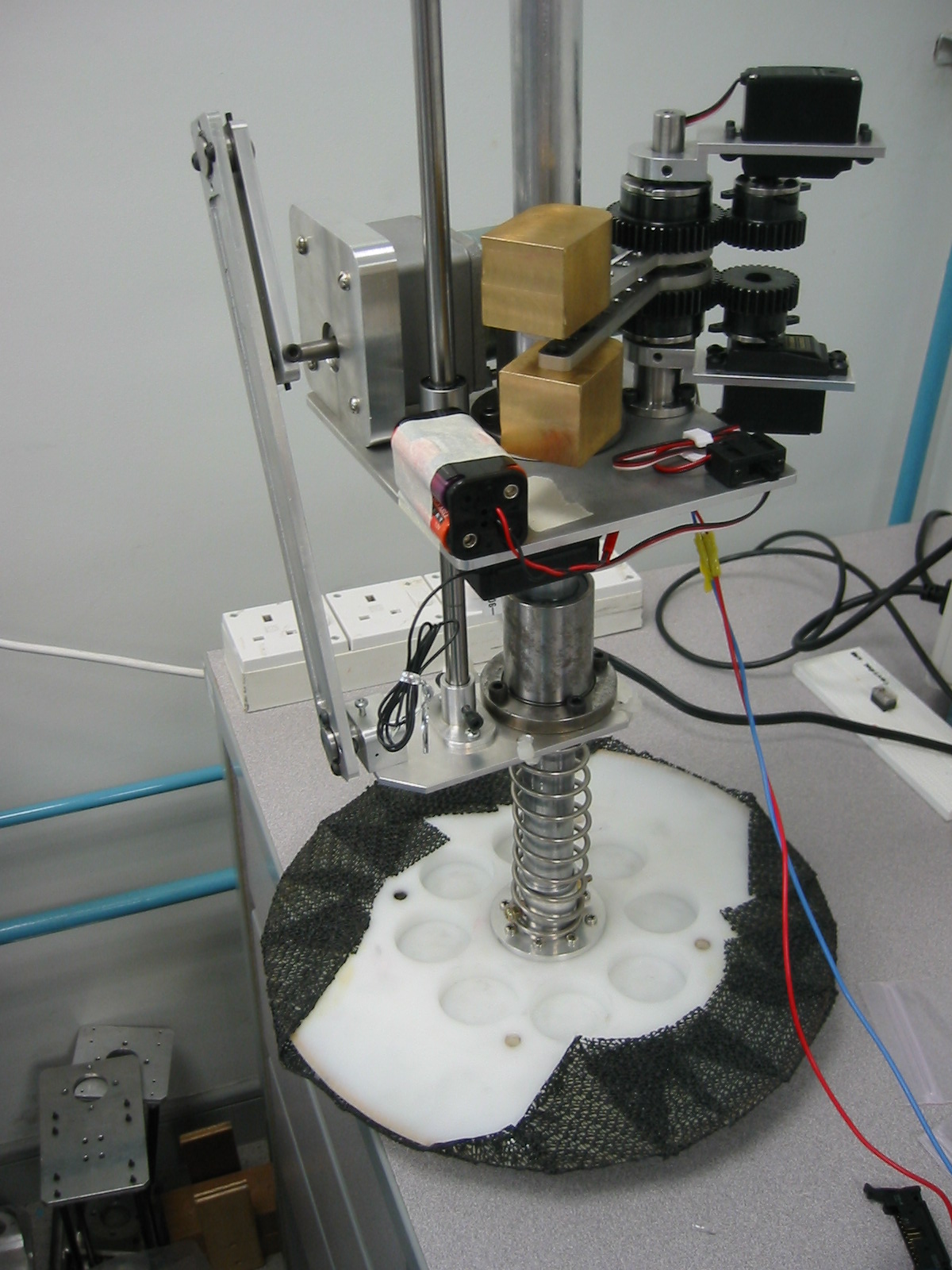
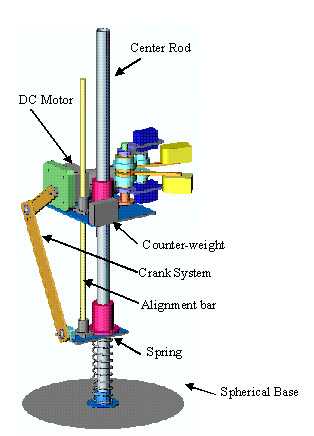
The purpose of this project is to reconstruct and analyze a self-stabilizing monopod hopping system proposed by Robert P. Ringrose (1996). This system has no active electronic sensors to use for feedback in its stability control. Instead, there is an inherent dynamic stability during its movement that prevents the system from toppling over and could recover from minor disturbances. The first prototype of self-stabilizing legged robot is shown below. Basically it consists of a body mass attached to a foot by a linkage in series with a spring. This robot used to hop vertically on the spot with a hopping height of 50mm. The movie of this prototype in action can be downloaded from here [Video-CurvedFoot] Then improvement in the design was made and the second design of the self-stabilizing legged robot (SSR-II) was manufactured. The objectives of this robot are to achieve increment in the hopping height and to get directional motion. And also to analyze the parameters that would affect the movement of the system.
The design details of the prototype-II of the self stabilising robot is shown below
Data Sheet For Robot
Videos [New Videos Added!!] The simulation of SSR-II in Yobotics [Video-simulation] A movie of the SSR-II in action. [Video-hopping height] Directional hopping of SSR-II [Video-Directional hopping] SSR-II hopping in a garden [Video-garden hopping] |