|
Autonomous
biped walking robots are supposed to explore various unknown environments.
This requirement demands a precise control of the actuators such
that biped does not cause any damage to itself or the surroundings.
This
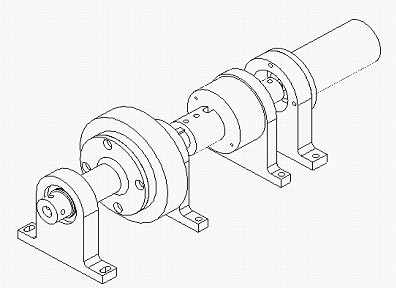
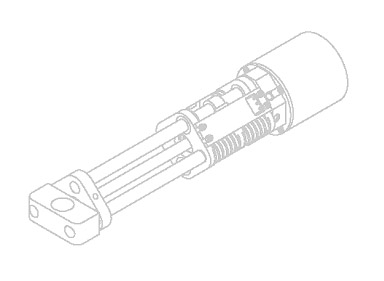
project is focussed on the force control of the actuators. Presently,
two different kinds of force controlled actuators are being studied:
Series Elastic actuators and Series Damper Actuators.
Series
Elastic Actuator (SEA)
Proposed
by MIT Leg Lab, it is an actuator that is connected to the external
load through an elastic component, for example, a spring. The desired
force on the load is achieved by controlling the deflection of the
elastic component. SEA have many desirable properties like high
force fidelity, low output impedance, shock absorption capability,
etc. The low system bandwidth has greatly limited its further applications
in industry.
Series
Damper Actuator
The
idea of this actuator system is similar to SEA, but the elastic
component is replaced with a damper in the actuator system. Accordingly,
the desired force is achieved by controlling the relative velocity
in the damper rather than the deflection of the elastic component.
The introduction of damper endows the system with impact protection,
larger bandwidth and output range and better performances, especially
at low output force range.
|